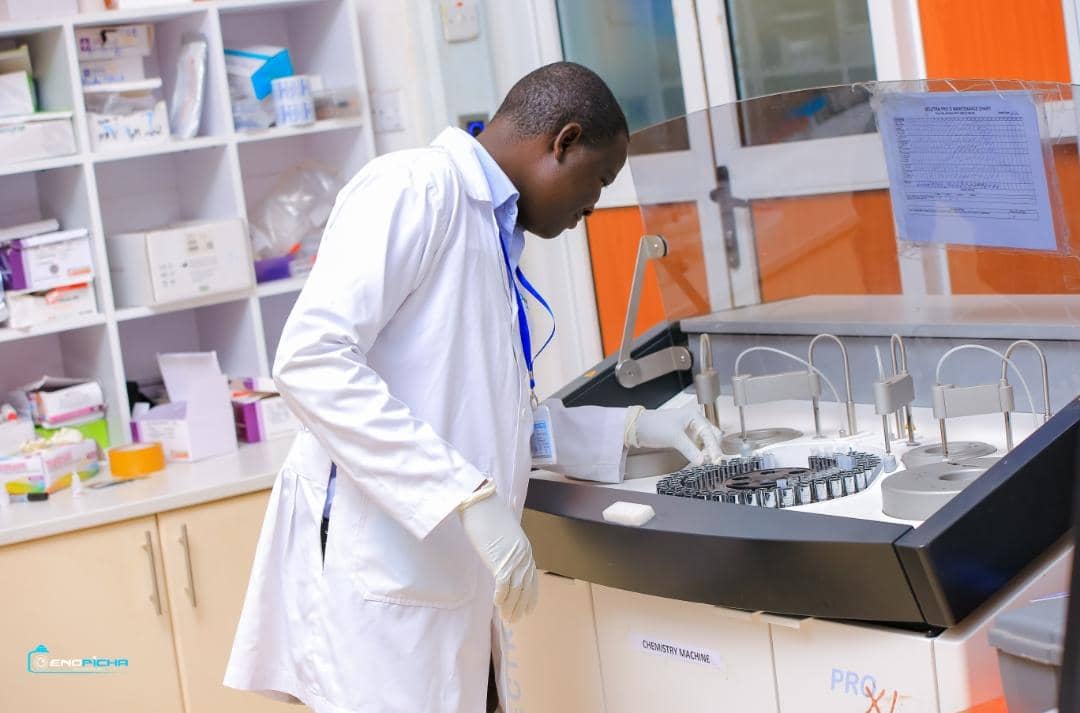
A renal panel is a group of tests that may be performed together to evaluate kidney (renal) function. The tests measure the amounts of various substances, including several minerals, electrolytes, proteins, and glucose (sugar), in the blood to determine the current status of the kidneys.
The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs that are located at the bottom of the ribcage in the right and left sides of the back. They normally filter about 170 litres of blood a day, removing waste products that form from the metabolism (breakdown) of food and from normal cell activity. The kidneys form urine to expel excess water from the body together with these waste products that are removed from the blood.
The kidneys help regulate pH and the amounts of necessary chemicals in the body including potassium, sodium, calcium, phosphorus, chloride, and bicarbonate (TCO2) by separating them out from the waste materials and releasing them back into the blood, getting rid of only as much or as little as needed to maintain normal blood concentrations.
If the kidneys are not functioning properly, waste products can accumulate in the blood and the amount of fluid can increase to dangerous levels, causing damage to the body or a potentially life-threatening situation. Numerous conditions and diseases can result in damage to the kidneys. The most common causes of and main risk factors for kidney disease are diabetes and hypertension. For more on the types and causes, see the article on Kidney Disease.
The individual tests included in a renal panel can vary by laboratory, but the tests typically performed include:
Blood Tests
Electrolytes – electrically charged chemicals that are vital to normal body processes, such as nerve and muscle function; among other things, they help regulate the amount of fluid in the body and maintain the acid-base balance. Electrolytes include:
Minerals
Protein
Waste products
Sugar
Two calculated values may also be reported with a renal panel:
Urine Tests
There are other laboratory tests that can be used to assess kidney function, including a urinalysis, urine protein or creatinine clearance. For those with diabetes or high blood pressure (hypertension), a urine albumin (microalbumin) test, which measures small amounts of albumin leakage from the blood into the urine, may also be used to detect early kidney damage. When both albumin and creatinine are measured in a random urine sample, an albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR) can be calculated. This may be done to more accurately determine how much albumin is escaping from the kidneys into the urine.
Request was sent